Bone Grafting
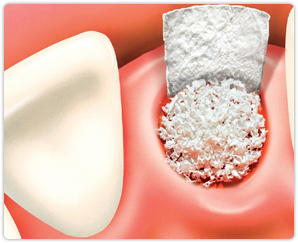
Periodontal disease is the leading cause of bone loss in the oral cavity. The bone grafting procedure is an excellent way to replace lost bone tissue and encourage natural bone growth.
Bone grafting is a versatile and predictable procedure which fulfills a wide variety of functions. A bone graft may be required to create a stable base for dental implant placement, to halt the progression of gum disease or to make the smile appear more aesthetically pleasing.
Types of bone grafting:-
There are several types of dental bone grafts. The following are the most common:
- Autogenous bone graft:- In this type of graft the bone is removed from elsewhere in the body and implanted in the mouth.
- Allograft:– Synthetic bone (man made) can be created in the laboratory and used in the bone grafting procedure.
- Xenograft:– This is the implantation of cow bone. A xenograft is perfectly safe and has been used successfully for many years. Ample bone can be obtained and no secondary donor site is necessary.
What happens in bone grafting treatment?
Bone grafting is a fairly simple procedure which may be performed under local anesthetic; however if large amounts of bone area need to be grafted, general anesthetic may be required.
Initially, the grafting material is prepared for insertion. A small incision is made in the gum tissue and then gently separated from the bone. The bone grafting material is then placed at the affected site.